In this chapter, we learn about the details of the 3 particles of an atom-- Protons, Neutrons and Electrons.
Relative Mass:
Protons: 1
Neutrons: 1
Electrons: 1/2000
The atomic model consist of a nucleus containing Neutrons and Protons, and it also consist of electrons revolving (orbiting) around the shells.
Shells are also called energy level.
Atomic number = Number of Protons
Mass Number = Number of Protons + Neutrons
Isotopes are atoms of the same element and atomic number but different mass numbers.
Isotopes have the same number of protons, electrons, atomic number and chemical properties but it has different number of neutrons, mass numbers and physical properties.
Formation of Cations: When an atom loses 1 or more electrons, it becomes a positively charged particle called Cation.
Formation of Anions: When an atom gains 1 or more electrons, it becomes a negatively charged particle called Anion.
This topic is quite interesting but it is very theoretical as there is not experiment for us to do. I understand this topic very well and find it quite interesting and rather easy.
-----------------------------------------------------------
Chapter 1.2 Periodic Table
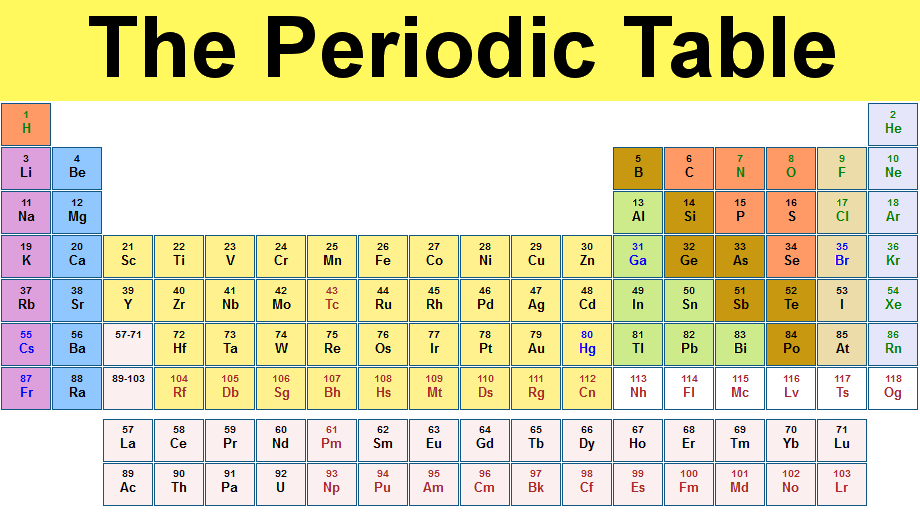

The picture above me shows a diagram of the periodic table.
This table is created by Mendeleev.
The vertical columns of similar elements are called groups.
The horizontal rows of elements are called period.
Group I--> Alkali Metals
Group II--> Alkali Earth Metals
Group VII--> Halogens
Group 0--> Noble gases
The number of valence electrons an atom has depends on its group number.
No comments:
Post a Comment